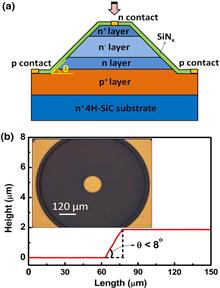
Ultraviolet (UV) detectors with large photosensitive areas are more advantageous in low-level UV detection applications. In this Letter, high-performance 4H-SiC p-i-n avalanche photodiodes (APDs) with large active area (800 μm diameter) are reported. With the optimized epitaxial structure and device fabrication process, a high multiplication gain of 1.4 × 106 is obtained for the devices at room temperature, and the dark current is as low as ~10 pA at low reverse voltages. In addition, record external quantum efficiency of 85.5% at 274 nm is achieved, which is the highest value for the reported SiC APDs. Furthermore, the rejection ratio of UV to visible light reaches about 104. The excellent performance of our devices indicates a tremendous improvement for large-area SiC APD-based UV detectors. Finally, the UV imaging performance of our fabricated 4H-SiC p-i-n APDs is also demonstrated for system-level applications.
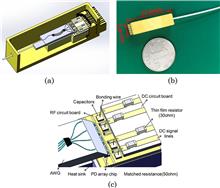
An ultra-compact hybrid-integration receiver optical subassembly (ROSA) with four channels is demonstrated in our laboratory with the size of 23.3 mm × 6.0 mm × 6.5 mm. The ROSA is comprised of a planar lightwave circuit (PLC) arrayed waveguide grating (AWG) chip, a top-illuminated positive-intrinsic-negative photodetector array chip, and a three-dimensional microwave circuit that is specially designed for compact packaging. For each transmission lane, the 3 dB bandwidth of the ROSA is up to 20 GHz, and the maximum responsivity is up to 0.53 A/W. The proposed package structure can be used for smaller package sizes and would be an easy assembling solution for 100 GbE optical communication devices.
The impulse response for a phase-change material Ge2Sb2Te5 (GST)-based photodetector integrated with a silicon-on-insulator (SOI) waveguide is simulated using finite difference time domain method. The current is calculated by solving the drift-diffusion model for short pulse (~10 fs) excitation for both of the stable phases. Full width at half-maximum values of less than 1 ps are found in the investigation. The crystalline GST has higher 3 dB bandwidth than the amorphous GST at a 1550 nm wavelength with responsivities of 21 A/W and 18.5 A/W, respectively, for a 150 nm thick GST layer biased at 2 V. A broad spectrum can be utilized by tuning the device using the phase-change property of material in the near infrared region.
Previous research shows that few-cycle laser (FCL) pulses with low energy and without a bias field can be used to coherently detect terahertz (THz) pulses. As we know, it is very difficult to stabilize the carrier envelope phase (CEP) of FCL pulses, i.e., there are some random fluctuations for the CEP. Here we theoretically investigate the influence of such instability on the accuracy of THz detection. Our results show that although there is an optimum CEP for THz detection, the fluctuations of the CEP will lead to terrible thorns on the detected THz waveform. In order to solve this problem, we propose an approach using two few-cycle laser pulses with opposite CEPs, i.e., their CEPs are differed by π.
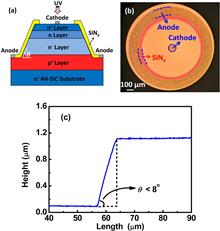
In this Letter, we report large-area (600 μm diameter) 4H-SiC avalanche photodiodes (APDs) with high gain and low dark current for visible-blind ultraviolet detection. Based on the separate absorption and multiplication structure, 4H-SiC APDs passivated with SiNx instead of SiO2 are demonstrated for the first time, to the best of our knowledge. Benefitting from the SiNx passivation, the surface leakage current is effectively suppressed. At room temperature, high multiplication gain of 6.5×105 and low dark current density of 0.88 μA/cm2 at the gain of 1000 are achieved for our devices, which are comparable to the previously reported small-area SiC APDs.
We report the terahertz (THz) wave generation from a single-color scheme modulated by pre-ionized air plasma via an orthogonal pumping geometry. It is found that the amplitude of the THz signal generated by the pump beam tends to decrease gradually with the increase of the modulation power. We believe that the ponderomotive force plays an important role in the process of the interaction between the pump beam and the pre-ionization beam. The hydrostatic state of the electrostatic separation field caused by the modulation beam will directly affect the generation efficiency of the THz wave. Our results contribute to further understanding of the theoretical mechanism and expanding of the practical applications of THz wave generation and modulation.
A infrared light trapping structure combining front subwavelength gratings and rear ZnO:Al nanoparticles for a PtSi Schottky-barrier detector over a 3–5 μm waveband is theoretically investigated. By selecting the proper plasmonic material and optimizing the parameters for the proposed structure, the absorption of the PtSi layer is dramatically improved. The theoretical results show that this improvement eventually translates into an equivalent external quantum efficiency (EQE) enhancement of 2.46 times at 3–3.6 μm and 2.38 times at 3.6–5 μm compared to conventional structures. This improvement in the EQE mainly lies in the increase of light path lengths within the PtSi layer by the subwavelength grating diffraction and nanoparticle-scattering effects.
Solar-blind ultraviolet detection is of great importance in astronomy and industrial and military applications. Here, we report enhanced solar-blind ultraviolet single-photon detection by a normal silicon avalanche photodiode (Si APD) single-photon detector with a specially designed photon-collecting device. By re-focusing the reflected photon from the Si chip surface on the detection area by the aluminum-coated hemisphere, the detection efficiency of the Si APD at 280 nm can be improved to 4.62%. This system has the potential for high-efficiency photon detection in the solar-blind ultraviolet regime with low noise.
High-speed cameras are widely used in experimental research and industrial measurement. Although multiple cameras are commonly used, whether the cameras are triggered at the same time is typically overlooked. This study measures the startup time difference between two high-speed cameras employing a proposed measuring system. A series of comparative experiments was conducted to consider the complex factors that can lead to a time difference. The system recorded the startup time differences for different combinations of two cameras at different frame rates, and thus acquired the dependence of the time difference on these factors. Suggestions are made on the basis of the experimental results.
Signal distortion due to the non-uniform response of the detector degrades the measurement accuracy of most metrology instruments. In this Letter, we report a newly developed calibration source system for reference-based non-uniformity correction using a laser source, a fiber, and a diffusive module. By applying the Monte Carlo simulation, we show that the transmittance of the system highly depends on the cavity reflection of the diffusive module. We also demonstrate the use of this system to achieve a flat field at a very low non-uniformity (less than 0.2%) with proper illumination intensity, which most costly commercial integrating sphere systems traditionally cannot provide.
Nonlinear dynamics in an optoelectronic delayed feedback semiconductor laser and its application in sensing are studied. We analyze the theories of stability and period of the laser. A route to quasi-periodic bifurcation or a stochastic state from stability is numerically analyzed by shifting the feedback level. The induced dynamics are found to be in one of four distributions (stable, periodic pulsed, period-three pulsed, and undamping oscillating). An external injection into the laser results in the process being more or less the opposite with the conventional optical injection cases. Based on this process or the dynamic regimes, we present a modeling of the incoherent detection sensor using the nonlinear period-one characteristic of the laser. The sensor discriminates the injection light variation as a sensing signal via detecting the behaviors from the period-one laser.
We propose and demonstrate a pseudo Fabry–Pérot filter in the terahertz frequency range of 0.1–0.5 THz. It consists of alternative liquid crystal layers and metallic slats. Separate sharp resonant peaks are shown in the simulated transmission spectra, and their positions shift toward higher frequencies when the refractive index of liquid crystal decreases. The measured transmission spectra are consistent with corresponding simulations. Via thermally tuning the refractive index of the filled liquid crystal, the resonant transmission frequencies shift accordingly. The work supplies a novel design for tunable terahertz filters, which would play important roles in terahertz imaging, sensing, high speed communication, and security applications.
Using the first-principles method based on the density functional theory (DFT), the work function of seven different GaN (0001) (1×1) surface models is calculated. The calculation results show that the optimal ratio of Cs to O for activation is between 3∶1 and 4∶1. Then, Cs/O activation and stability testing experiments on reflection-mode negative electron affinity GaN photocathodes are performed. The surface model [GaN (Mg): Cs] Cs-O after being activated with cesium and oxygen is used. The experiment results illustrate that the adsorption of O contained in the residual gas increases the surface potential barrier and the reduction of the effective dipole quantity is the basic cause of the quantum efficiency decay.
We propose a system of time-division multiplexing (TDM) and spatial frequency-division multiplexing (SFDM). Extrinsic Fabry–Perot interferometric sensors are applied to detect weak acoustic signals. The broadband source is employed, the light from it is modulated by a pulse signal sequence and is efficiently amplified by semiconductor optical amplifiers. Experimental results show that the equivalent noise pressure spectrum level is -97.2 dB re 1 rad/vHz below 1250 Hz, and the cross talk between two sensors in one TDM channel is -32.7 dB with a cavity length difference of 60 μm. The number of sensors in this multiplexing system can theoretically reach 160.
Photoresponse of large-area multi-walled carbon nanotube (MWCNT) films is explored under laser illumination. The experiment shows that the photo-induced current shows nearly linear response to the bias voltage. The photocurrent depends on the laser illumination spot position, with the maximum photocurrent occurring at the metal–film interface, while the minimum photocurrent is observed between two electrodes. We are attributing this photo-generated exciton due to Schottky junction between Al electrodes and the CNTs, and electron's concentration effect. The sample device shows photo responsibility of 521 mA/W at a bias voltage of 2V, which indicates that this device can be developed as a position-sensitive photodetector.
This paper proposes a novel method of multibeam laser heterodyne measurement for an electrostriction coefficient. Based on the Doppler effect and heterodyne technology, loaded with the information of length variation to the frequency difference of the multibeam laser heterodyne signal by the frequency modulation of the oscillating mirror, this method can obtain many values of length variation caused by different voltages after the multibeam laser heterodyne signal demodulation simultaneously. Processing these values by a weighted-average method, it can obtain length variation accurately, and eventually obtain value of electrostriction coefficient of metal by the calculation. This novel method is used to simulate measurement for electrostriction coefficient of PZT under different voltages by MATLAB, and the obtained result shows that the relative measurement error of this method is just 0.98%.
A series of Alx-(Alq3)1-x granular films is prepared on Si wafer with native oxide layer using co-evaporation technique. Large lateral photovoltaic effect (LPE) is observed, with an optimal LPV sensitivity of 75 mV/mm in x = 0.35 sample. The dependence of LPE on temperature and Al composition is investigated, and the possible mechanism is discussed.
Two-dimensional metallic photonic crystal slabs with square lattice are proposed to be used for the design of waveguide bandpass filters operating in millimeter to terahertz region. Filter characteristics are studied when rod radii and lattice constants are changed. Based on the frequency scaling technique, a series of higher frequency filters has been designed. By using laser drilling and welding processing techniques, a compact waveguide filter embedded in an EIA-WR10 waveguide with central frequency 145.5 GHz and 3-dB bandwidth of 5.26 GHz is fabricated and measured. The measurement data agree well with the simulation prediction.
We present high power terahertz quantum laser at about 3 THz based on bound-to-continuum active region design. At 10 K, corrected by the collection efficiency, the maximum peak power of 137 mW is obtained in pulsed mode. What’s more, we firstly introduce monolithically integrated THz quantum cascade laser (QCL) array and the maximum peak power increased to 218 mW after correction. In total, the array shows better performance than single device, implying cheerful prospect.
Terahertz wave detecting method based on multi-reflection optical lever with nano-scale displacement measuring precision is presented. Multi-reflection optical lever is composed of a pair of plane micro-mirrors, and detecting material is coated on one mirror to absorb terahertz radiation. Affected by radiant thermal effects, tiny mirror deformation is produced while displacement between mirrors is changed. These variations proportional to radiation are amplified and measured by multi-reflection optical lever, and then terahertz wave power can be obtained. Theoretical displacement measuring precision of multi-reflection optical lever method is better than 1 nm. Experimental results show that measuring stability of this method is better than Knife-edge filter method. This method achieves resolution of 4 nm, sensitivity of 5.95 nm/mV, and measurement range of 30 \mu m.
In order to achieve the goal of the autonomous landing of fixed-wing unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), a new method is put forward for using the monocular camera on board to provide the information, which is need for landing. It is not necessary to install additional equipment in the airport. The vision-based method only makes use of the two edge lines on both sides of the main runway and the front edge line of the airport without using the horizon. While the runway width is known, the method can produce the attitude and position parameters of landing. The results of the hardware-in-the-loop simulation show the proposed method has better accuracy and faster computation speed.
Ultrasonic thermography or thermosonics is proved to be an effective non-destructive testing (NDT) method for inspecting carbon-fiber-reinforced polymer (CFRP) composites; however, the potential damages for the structure cannot be ignored, because of the contact vibration between the ultrasonic horn and the specimen. This work aims at developing a new excitation method for ultrasonic thermography—air-coupled ultrasonic excitation. CFRP laminates with impact damages are tested by air-coupled ultrasonic thermography, and the theoretical model of heat conduction is given. Results demonstrate good excitation performance for impact damages detection in CFRP composites. Moreover, the conventional ultrasonic thermography results are shown, and the prospect of air-coupled ultrasonic thermography is discussed.
The intensifying process of polarization effect at room temperature in a pixellated Cadmium zinc telluride (CdZnTe) monolithic detector is studied. The process is attributed to the increase in build up space charges in the CdZnTe crystal, which causes an expansion of the space charge region under the irradiated area. The simulations of electric potential distributions indicate that the distorted electric potential due to the high X-ray flux is significantly changed and even deteriorated due to increasing space charges within the irradiated volume. An agreement between the space charge distribution and electric potential is discussed.
The pulse time of arrival (TOA) is a determining parameter for accurate timing and positioning in X-ray pulsar navigation. The pulse TOA can be calculated by comparing the measured arrival time with the predicted arrival time of the X-ray pulse for pulsar. In this study, in order to research the measurement of pulse arrival time, an experimental system is set up. The experimental system comprises a simulator of the X-ray pulsar, an X-ray detector, a time-measurement system, and a data-processing system. An X-ray detector base is proposed on the basis of the micro-channel plate (MCP), which is sensitive to soft X-ray in the 1–10 keV band. The MCP-based detector, the structure and principle of the experimental system, and results of the pulse profile are described in detail. In addition, a discussion of the effects of different X-ray pulse periods and the quantum efficiency of the detector on pulse-profile signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is presented. Experimental results reveal that the SNR of the measured pulse profile becomes enhanced as the quantum efficiency of the detector increases. The SNR of the pulse profile is higher when the period of the pulse is smaller at the same integral.